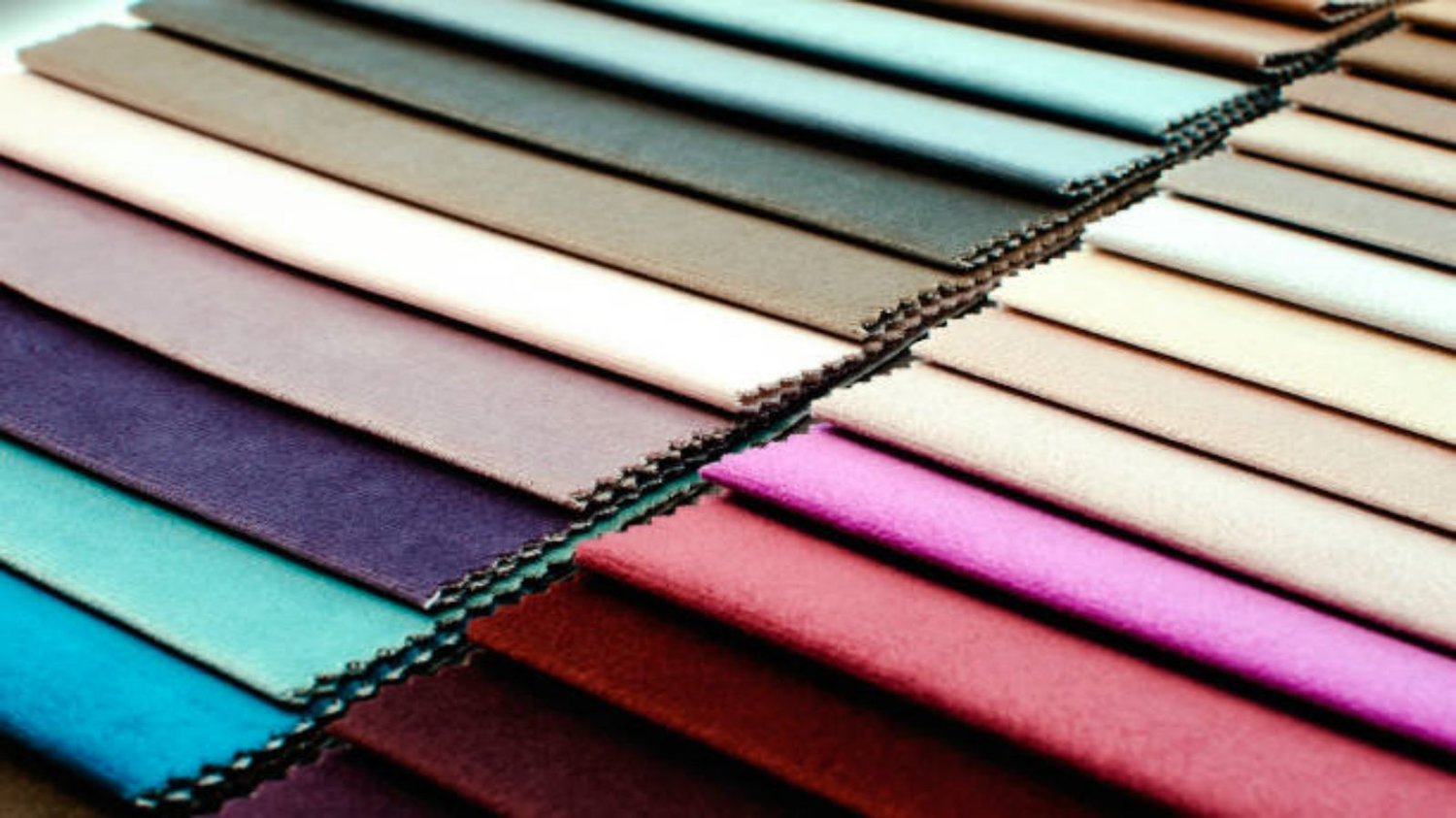
Fabric Finishing & Treatments: Process & Methods
Introduction
Fabric finishing and treatments play a crucial role in enhancing the functionality and appearance of textiles. Whether it is to improve durability, add special properties, or alter the aesthetic appeal, various processes and methods are utilized. In this article, we will explore the different aspects of fabric finishing and treatments, providing valuable insights into the techniques and their applications.
Preparation: Cleaning and Inspection
Before any fabric finishing or treatment process begins, thorough cleaning and inspection are essential. This step ensures that the fabric is free from any contaminants, such as dirt, oils, or stains, which may hinder the subsequent processes. Inspection helps identify any pre-existing flaws or damages that need to be addressed before proceeding.
Chemical Treatments: Dyeing and Printing
Dyeing and printing are two common chemical treatments used to add color and patterns to fabrics. Dyeing involves immersing the fabric in a dye solution, allowing the color to penetrate the fibers. Printing, on the other hand, applies color in specific patterns using techniques like screen printing or digital printing. Both processes require precise control of temperature, dye concentration, and time to achieve desired results.
Physical Treatments: Calendering and Embossing
Physical treatments like calendering and embossing alter the surface texture of fabrics. Calendering involves passing the fabric through heated rollers to impart a smooth, glossy appearance. Embossing, on the other hand, uses engraved rollers or plates to create raised or recessed patterns on the fabric. These treatments enhance the fabric's aesthetics and can also improve its hand feel.
Chemical Finishes: Water Repellency and Flame Retardancy
Chemical finishes are applied to fabrics to impart specific properties. Water repellency treatments, for example, use chemicals that create a barrier on the fabric surface, preventing water from penetrating. Flame retardant finishes, on the other hand, inhibit the spread of flames, making the fabric more resistant to fire. These finishes are crucial in applications where protection against water or fire is required.
Mechanical Finishes: Crease Resistance and Wrinkle Recovery
Mechanical finishes are designed to improve the fabric's performance and appearance through physical manipulation. Crease resistance finishes, for example, use resin-based treatments that enhance the fabric's ability to resist wrinkling and creasing. Wrinkle recovery finishes, on the other hand, help fabrics regain their original shape after being subjected to deformation. These finishes are particularly useful in garments and home textiles.
Antimicrobial Treatments: Odor Control and Hygiene
With the growing focus on hygiene and odor control, antimicrobial treatments have gained significant importance. These treatments use chemicals that inhibit the growth of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms on the fabric surface, reducing the risk of odor formation and maintaining better hygiene. Antimicrobial treatments are commonly applied to sportswear, activewear, and healthcare textiles.
Specialty Finishes: UV Protection and Moisture Management
Specialty finishes cater to specific needs and requirements of fabrics. UV protection finishes, for instance, incorporate chemicals that absorb or reflect harmful ultraviolet rays, reducing the risk of skin damage. Moisture management finishes, on the other hand, enhance the fabric's ability to wick away moisture, keeping the wearer dry and comfortable. These specialty finishes are highly sought after in outdoor and performance textiles.
Testing and Quality Control
Throughout the fabric finishing and treatment process, rigorous testing and quality control measures are crucial to ensure the desired outcomes are achieved. Various parameters, such as colorfastness, durability, and performance, are assessed through standardized tests. This helps identify any issues and ensures that the finished fabric meets the required specifications and standards.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Practices
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainable fabric finishing and treatment methods. Eco-friendly practices focus on reducing water consumption, minimizing chemical usage, and adopting energy-efficient processes. Innovations in this field include the use of natural dyes, bio-based finishes, and recycling of wastewater. These sustainable practices aim to minimize the environmental impact of fabric finishing and treatments.
Conclusion
Fabric finishing and treatments encompass a wide range of processes and methods that enhance the functionality, aesthetics, and performance of textiles. From chemical treatments to physical finishes, each step plays a vital role in creating fabrics with desirable properties. By understanding the various techniques and their applications, manufacturers and consumers alike can make informed decisions about the fabrics they choose and the benefits they offer.